Which Best Describes the Multiregional Model for Human Evolution
This model also predicts that regional morphological patterns are stable reflecting absence of. 1 C is slightly favored with a posterior probability of 0461 over MRE with two population sizes in AfricaAsia MRE2S 0422.

Multiregional Origin Of Modern Humans Wikiwand
Which best describes the multiregional model for human evolution.

. Multiregional evolution is a hypothesis that addresses the pattern of Pleistocene evolution in hominids a lineage with identi able geographic variation at. Thorne and Milford H. By 115000 years ago early modern humans had expanded their range to South Africa and into Southwest Asia Israel shortly after 100000 years ago.
The Multiregional Model of modern human origins predicts that a group of features recognized as characterizing the evolution of regional populations from their archaic regional ancestors will consistently show higher incidence in those regions. 1Homo sapiens is the sole survivor among a diversity of coexisting Homo species. The human range as the punctuational model requires.
The multiregional hypothesis multiregional evolution MRE or polycentric hypothesis is a scientific model that provides an alternative explanation to the more widely accepted Out of Africa model of monogenesis for the pattern of human evolution. 3 Each region equally genetically. There is no reliable evidence of modern humans elsewhere in the Old World until 60000-40000 years ago during a short temperate period in the midst of the last ice age.
The multiregional continuity model suggests that local populations in Europe Asia and Africa continued their indigenous evolutionary development from premodern Middle Pleistocene forms to anatomically modern humans. The multiregional hypothesis argues that scientists. This hypothesis suggests that Homo erectus slowly wandered out of Africa and.
The Evolution of Modern Humans Two origins are considered when thinking about the evolution of modern humans. The candelabra model multiregional evolution the replacement model and the assimilation model. Four models have been used to describe the evolution of modern humans from archaic predecessors.
The original multiregional model of human evolution redrawn from Weidenreich 1946. Modern humans developed in many different places simultaneously. Which of the following best describes human Homo evolution.
Key fossils and sites known at the time are placed in a trellis with vertical lines indicating regional descent and diagonal and horizontal lines representing genetic exchange between regions. The Multiregional Evolution of Humans Both fo ssil and genetic evidence argues that various human groups arose where they are fo und today by Alan G. Describe these four hypothetical models of human evolution.
The disagreement centered on whether the fossil Ramapithecus was. Three predictions if divergence 1 million years ago 2 Split one million years ago. Classic multiregionalism is about geographical continuity and variations of it have been linked to beliefs that there are real autochthonous people.
Howells suggested NoahsArkas one ofseveral possibilities for the explanation ofmodern population origins and. Wolpoff T W o decades ago paleoanthropol ogists were locked in a debate about the origin of the earliest humans. Multiregional models of the origins of modern humans predict that we should first see modern human fossils in Africa Both the Replacement and Multiregional Models of human origins agree that there was an initial dispersal of Homo erectus from Africa into the rest of the Old World.
Homo erectus The Multiregional Model The multiregional model suggests that Homo sapiens didnt evolve at a specific time or place instead they slowly evolved from Homo erectus right an ancestor of the modern human that lived between 800000 and 18million years ago all. Multiregional model posits that modern humans evolved simultaneously in Asia Africa and Australia. A Now-Discredited Theory of Human Evolution The Multiregional Hypothesis model of human evolution abbreviated MRE and known alternatively as Regional Continuity or Polycentric model argues that our earliest hominid ancestors specifically Homo erectus evolved in Africa and then radiated out into the world.
Theres the Multiregional Model that concentrates on a multiple origins theory in which the different human populations or races had independent origins and evolved in isolation from each other and theres the recent single-orgin hypothesis or the Out of Africa. The multiregional hypothesis states that independent multiple origins Model D or shared multiregional evolution with continuous gene flow between continental populations Model C occurred in the. Finally the fact that the best-fitting models in these.
African replacement model versus Multiregional evolution model. Among the multiregional evolution MRE models the MRE with bottleneck and instantaneous population growth MREBIG model Fig. Multiregionalism or the Multiregional Evolution MRE hypothesis is a model of Pleistocene human evolution which argues the human species emerged in Africa 2 million years ago and developed their modern forms in every area of the Old World.
The first or the multiregional hypothesis states that Homo sapiens evolved from Homo erectus outside of Africa. Human evolution Multiregional model of human origins Hominins across Old World were a single species connected by gene flow Multiregional differences the result of local adaptation Out-of-Africa model of human origins All human populations are derived from recent African ancestry Phylogenetic data supports Out-of-Africa model.

Out Of Africa Versus The Multiregional Hypothesis World Library Of Science
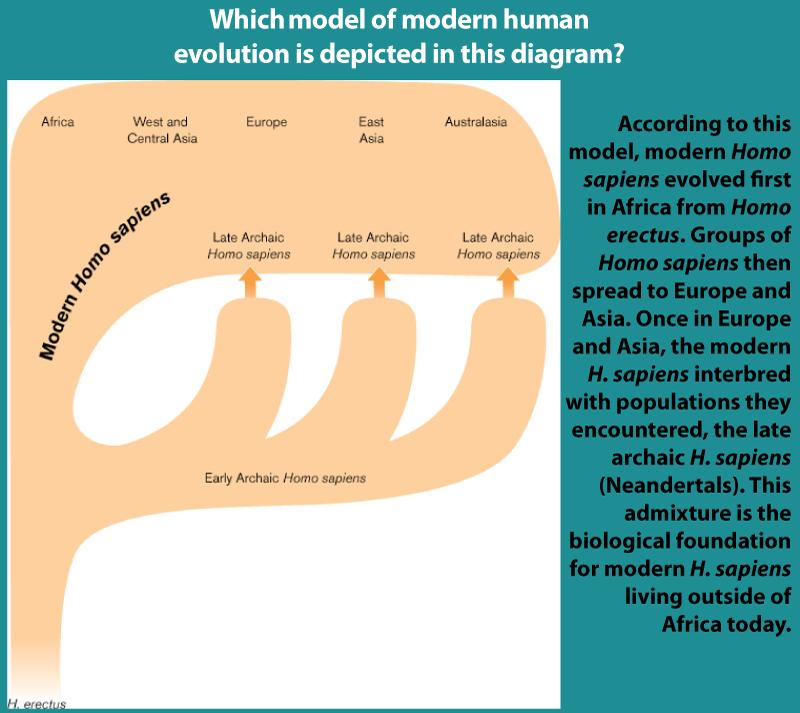
Anth 102 Chapter 12 The Origins Evolution And Dispersal Of Modern People Flashcards Chegg Com

No comments for "Which Best Describes the Multiregional Model for Human Evolution"
Post a Comment